What is the difference between polycarbonate and PMMA?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Sep 11,2019
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They easily work, molded, and transformed.
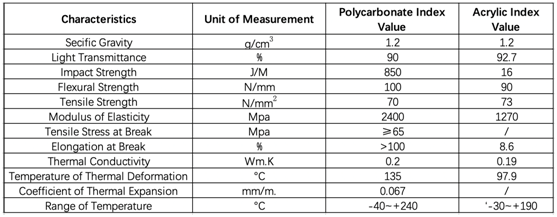
Polycarbonate is a durable material. Although it has high impact-resistance, it has low scratch-resistance. Therefore, a hard coating is applied to polycarbonate eyewear lenses and polycarbonate exterior automotive components. The characteristics of polycarbonate compare to those of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA, acrylic), but polycarbonate is stronger and will hold up longer to extreme temperature. Polycarbonate is highly transparent to visible light, with better light transmission than many kinds of glass. Transmits up to 90% visible light.
What is PMMA?
Poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, or plexiglass as well as by the trade names Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Lucite, and Perspex among several others, is a transparent thermoplastic often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It’s an important optical plastic.
PMMA is a strong, tough, and lightweight material. It also has good impact strength, higher than both glass and polystyrene; however, PMMA's impact strength is still significantly lower than polycarbonate and some engineered polymers. But it has low surface hardness and easy scratching, and absorbing water is easy to swell.
Polycarbonate & PMMA(Acrylic)
Characteristics